Boosting Shale Gas: Pipe Depth Secrets Revealed!
Introduction to Shale Gas Extraction
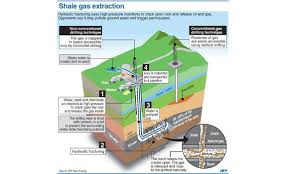
Shale gas has become a cornerstone of the global energy revolution, offering a cleaner-burning fossil fuel alternative to coal. Extracted from fine-grained sedimentary rock formations, its production relies on advanced techniques like horizontal drilling and hydraulic fracturing. While much attention is often given to fracking fluids and drilling angles, an equally critical but lesser-known factor is pipe depth—a technical element that can make or break efficiency in shale gas operations.
The Science Behind Pipe Depth
Pipe depth refers to how far the wellbore extends vertically and horizontally into the shale formation. The proper depth ensures optimal access to gas-rich zones while avoiding non-productive layers. If a pipe is set too shallow, it may bypass rich gas pockets; too deep, and the well risks technical complications and cost overruns. Engineers use geological surveys and seismic imaging to determine the "sweet spot" for maximum extraction. The ability to target this depth precisely translates directly to production volume and economic return.
Impact on Gas Yield and Pressure
Well depth directly influences the reservoir pressure and ultimately, the gas yield. Deeper wells often encounter higher pressure zones that can enhance initial gas flow. However, such depths also demand stronger casing and more robust pressure management systems. Some shale formations are more productive at specific depths—knowing exactly where to place the well pipe can significantly enhance both short-term output and long-term well sustainability.
Technological Advances in Drilling Precision
Advancements in directional drilling technologies have dramatically improved the industry’s ability to achieve the optimal pipe depth. Real-time data analytics, AI-assisted drilling controls, and smart sensors allow for micro-adjustments during drilling operations. These innovations not only improve accuracy but also reduce the risk of costly drilling errors. Companies that integrate depth-optimization algorithms into their operations often see improved efficiency and a higher return on investment.
Future Outlook and Environmental Considerations
As the industry evolves, understanding and leveraging pipe depth continues to be a key factor in sustainable shale gas development. Future strategies may include adaptive drilling technologies that adjust depth in response to live geological feedback. Moreover, optimizing pipe depth also has environmental implications—targeting the most productive zones reduces the number of wells needed, limiting surface disruption and water usage. In the race for cleaner, more efficient energy, the secret beneath our feet lies in drilling with depth—and purpose.
 :
:  :
:  :
: 

Comments
Post a Comment